

Rental Property Owner: Property and Financial Risks
If you are wondering about investing in real estate, you must have explored the possibility of becoming a rental property owner. Rental properties may be used mainly for residential purposes but can also be used as a business space. That said, passive income, equity growth, and tax benefits are attractive. But, just as with any investment, it is not without its share of property risks.
Investing in real estate is not a decision to be taken lightly. It requires exhaustive research, careful planning, and a cogent assessment of your financial situation and risk tolerance. Hence, let's explore what it means to be a rental property owner, the types of rental properties, and the inherent financial risks. By the end of this read, you'll be more equipped to make informed decisions in your property investment journey.
What Does it Mean to Be a Rental Property Owner?
Rental property ownership offers a path to long-term financial security, potentially providing a steady stream of income and appreciating asset value. This makes it an attractive choice for investors who prefer tangible investments. But not everything that glitters is gold. A rental property owner buys real estate for either of the two purposes: residential or commercial, but with the same intention: leasing it out to tenants.
The rental property owner would have to handle property maintenance and repair costs, insurance, and other expenses. But, in most cases, the tenant's rent is enough to earn a profit. However, rental ownership does not lead to smooth sailing and steady cash flow. Owning rental properties comes with its own set of financial and management challenges, or to put it simply, there are considerable property risks for a rental property owner to explore before they can comfortably invest.
Learn More:
Discover Your Next Rental Property Rental Properties:
The Six Examples You Must Know
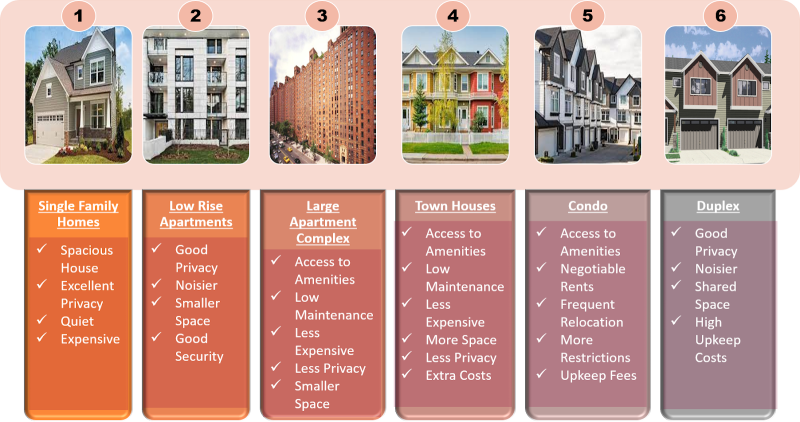
Talking about rental properties, you cannot miss out on knowing the six most common properties used as residential rental places. Each type of rental property comes with its pros and cons. But, the most fitting property for you would be the one that best caters to your needs.
Tips: Minimize Property Risks
Understanding and preparing for property risks is key to successful rental property ownership. Here's how you can mitigate some of these property risks:
Maintain a Reserve Fund: A well-stocked reserve fund can cover unexpected expenses or periods of vacancy. Experts suggest having a reserve covering at least six months of property expenses.
2. Thorough Tenant Background Check: Renting out a space that is one of your most significant investments should make you circumspective about who lives there. A thorough tenant screening process can minimize the probability of problematic tenants. Look for reliable rental history, good credit, and solid references.
3. Regular Property Maintenance: Keep your property in top condition to minimize major repairs and satisfy tenants. A satisfied and well-settled tenant is less likely to move, reducing vacancy risk.
4. Stay Abreast of Market Trends: Fluctuations are a salient real estate market feature. Stay aware of these changes and adjust your rental rates accordingly. If property values are decreasing, consider ways to add value to your property.
5. Understand Laws and Regulations: Stay updated on local and national laws related to rental properties to avoid legal issues and potential financial penalties.
6. Get the Right Insurance: Ensure you have sufficient coverage to protect against property damage, liability, and loss of rental income. Learn More: Check out a Property For Sale Near You
The Financial Benefits of Being a Rental Property Owner While we've covered the risks, let's not overlook the benefits that make being a rental property owner attractive:
Benefits of Rental Property Ownership
Benefits
Steady Cash Flow A rented property can provide regular income, which is a key attraction for many investors.
Property Appreciation Over time, your property will likely increase in value, leading to increased wealth.
Tax Deductions Your rental income can balance out the expenses like mortgage interest, property taxes, insurance, maintenance costs, and depreciation.
Equity Build-up If you have a mortgage, each payment (funded by the tenant's rent) increases your ownership stake in the property.
Inflation Hedge Real estate often serves as an effective hedge against inflation. As living costs rise, so do rents and property values. Control Unlike many other investments, real estate gives you direct control over your investment.
Bottom Line
As with any investment, becoming a rental property owner comes with its share of risks and rewards. Understanding and preparing for these property risks can help ensure your rental property venture is successful. Rental properties can be risky due to fluctuating rental rates, vacancy periods, and damage. Owning rental property can be dangerous due to property maintenance costs, property management costs, and the risk of property depreciation. By mitigating risks and leveraging the financial benefits, rental property owners can become a viable path toward building long-term wealth.
FAQs
1. What are the primary financial risks of owning a rental property? The main financial risks of owning a rental property include vacancy risks, maintenance and repair costs, dealing with bad tenants, market fluctuations, regulatory changes, and increased insurance costs.
2. How can I mitigate the risk of having bad tenants in my rental property? Conduct a thorough tenant background check, looking for reliable rental history, good credit, and solid references. This can minimize the likelihood of problematic tenants.
3. Are there any benefits to being a rental property owner? Yes, there are benefits to being a rental property owner, including steady cash flow, property appreciation, tax deductions, equity build-up, an inflation hedge, and direct control over your investment.
4. What percentage of rental property owners are individual investor Approximately 41% of all rental property owners are individual investors. Half of all rental properties comprise 1 to 4 units, and individual landlords own 72% of all 1 to 4 unit houses.
5. What is the biggest risk of owning a rental property? The most significant risk of owning a rental property is the potential for financial losses, which can result from various factors, including bad tenants who refuse to pay rent or other unexpected expenses.
